The Endocannabinoid System (SEC) is an intercellular communication system. Its function is to balance metabolic processes and improve the functions of our body. It is one more system, such as the circulatory system. The ECS plays a fundamental role in regulating our physiology, as well as our mood.
However, it is quite possible that you have never heard of it. This is because its discovery is quite close. In the 1990s, during a study on phytocannabinoids, it was discovered that most mammals, including humans, have cannabinoid receptors in our bodies. From then on, the research went deeper until in 1992 it found the first cannabinoid produced by the body naturally: anandamide, known as the molecule of happiness.
These discoveries, that of the cannabinoid receptors and that of anandamide, led to the discovery of the Endocannabinoid System.
How does CBD interact with the Endocannabinoid System?
The role of cannabinoids, such asCBD, is to bind and activate the receptors. CBD causes the function of the endocannabinoid system to improve so that it balances the rest of our organs.
What it does is enhance the effects of endocannabinoids, which are already present in our body.
It is important to be clear that we all have an endocannabinoid system and that it is active. The only thing CBD does is enhance its effects.
How does the Endocannabinoid System work?
Many times, to explain how the Endocannabinoid System works, the analogy of the key and the lock is used. It is the easiest way to understand how it works for all of us who have not studied neuroscience.
Endocannabinoids and receptors act like a lock and key. In such a way that the receptors would be the lock and the endocannabinoids would be its key.
Receptors are proteins present in the cell membrane and are the lock for endocannabinoids (cannabinoids that our body produces naturally). Endocannabinoids act like a key that binds to receptors to activate them.
The activation of the receptors produces changes within the cells that act in the Endocannabinoid System, which affects the physiological processes of the body.
For their part, phytocannabinoids (plant-produced cannabinoids) bind to this lock to enhance and enhance the effects of endocannabinoids.
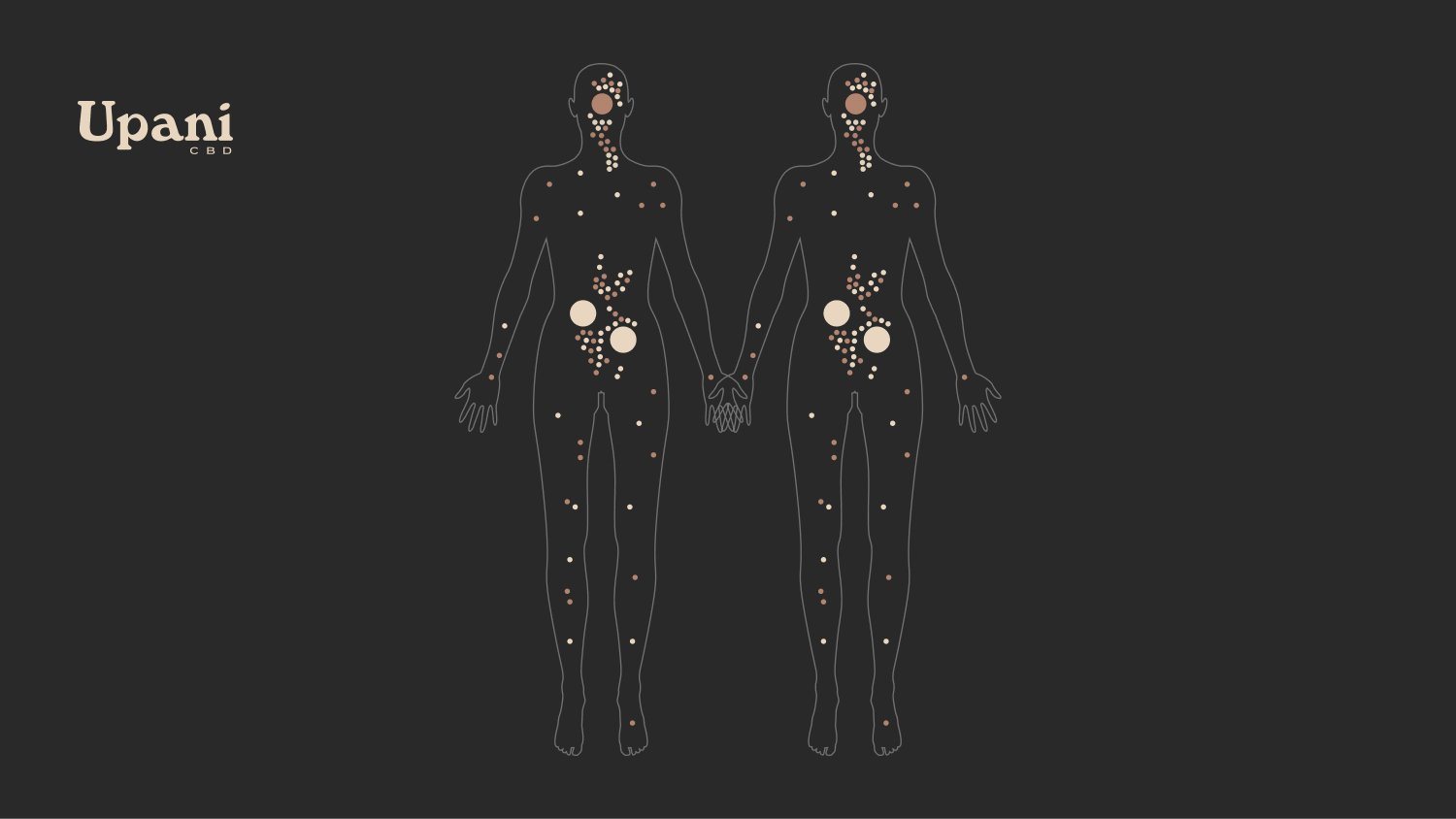
Where are receptors found and what is their function?
The first receptor discovered was CB1. It is found in the central nervous system and in a very abundant way in our brain. We can find the CB1 receptor in areas relevant to cognitive functions, such as attention, memory or language. Likewise, also in areas related to the emotional state, pain, sensory perception, visceral perception and motor coordination.
CB2 receptors have less studies and therefore very little is still known about them. However, they have been found to be found in the peripheral nervous system and are especially abundant in cells with immune function.
Likewise, GPR55 receptors are known to be involved in the regulation of blood pressure, as well as inflammatory pain and bone metabolism. These receptors are found in the digestive system, in the adrenal glands, and in the central nervous system.
TRPV receptors are responsible for the regulation of pain, inflammation, thermoregulation and muscle tone. They are found in all tissues and in the Central and Peripheral Nervous System.


